Overview
Inject visual indicators directly into web pages using content scripts - JavaScript that runs in the context of websites. This lesson adds a ribbon element to pages with notes, providing visible feedback beyond the extension icon.
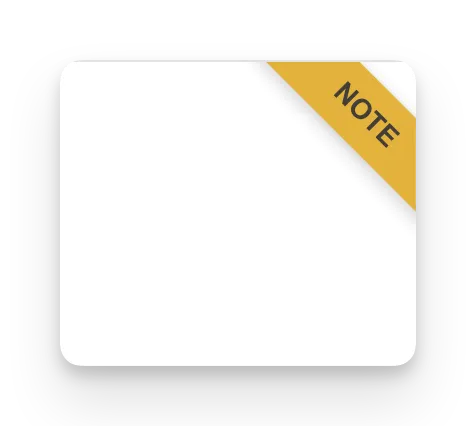
By the end, TabNotes will display “Note” ribbons on pages where users have saved notes.
What You’ll Learn
- Understand content scripts and isolated world execution
- Create static content script declarations in WXT
- Inject DOM elements into web pages
- Style content script elements with scoped CSS
- Match URLs with pattern matching syntax
- Handle content script lifecycle and timing
What Are Content Scripts?
Content scripts are JavaScript files that run in the context of web pages, allowing extensions to:
- Read and modify page DOM
- Inject custom UI elements
- Monitor user interactions on pages
- Extract data from websites
Isolated World Execution
Content scripts run in an isolated world separate from page JavaScript:
Benefits:
- Content scripts can’t interfere with page JavaScript
- Page JavaScript can’t interfere with content scripts
- Separate variable scopes prevent naming conflicts
Limitations:
- Can’t directly call page JavaScript functions
- Must use messaging for complex interactions
Content Script Injection Methods
Static Declaration (Manifest-Based)
Automatically inject scripts based on URL patterns:
{
"content_scripts": [{
"matches": ["https://*.nytimes.com/*"],
"js": ["content-script.js"],
"css": ["my-style.css"]
}]
}Pros: Automatic, runs on page load Cons: Less flexible, can’t conditionally inject
Dynamic Injection (Programmatic)
Inject scripts via API calls (Lesson 10 covers this):
await browser.scripting.executeScript({
target: { tabId: tab.id },
files: ['content-script.js']
});Pros: Full control, conditional injection Cons: Requires additional permissions, more complex
For TabNotes: Use static declaration - simpler and automatic.
Creating Content Scripts in WXT
WXT uses file-based routing for content scripts. Create entrypoints/content/index.ts:
// entrypoints/content/index.ts
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
main() {
console.log('Content script running on:', window.location.href);
}
});WXT Auto-Generation: This automatically adds to manifest:
{
"content_scripts": [{
"matches": ["https://*/*"],
"js": ["content-scripts/content.js"]
}]
}URL Pattern Matching
matches Array: Defines which URLs trigger the content script.
Common Patterns:
// All HTTPS sites
matches: ['https://*/*']
// All URLs (including chrome://, file://)
matches: ['<all_urls>']
// Specific domain
matches: ['https://github.com/*']
// Multiple domains
matches: ['https://github.com/*', 'https://gitlab.com/*']
// Subdomain wildcard
matches: ['https://*.google.com/*']For TabNotes: Use https://*/* to run on all HTTPS sites.
Injecting the Ribbon Element
Create a visual indicator that shows when pages have notes:
// entrypoints/content/index.ts
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
main() {
// Create ribbon element
const ribbon = document.createElement('div');
ribbon.id = 'tabnotes-ribbon';
ribbon.textContent = 'Note';
// Inject into page
document.body.appendChild(ribbon);
}
});Testing: Visit any HTTPS site - “Note” appears unstyled on page. At the very end of the page.
Styling Content Script Elements
Creating the CSS File
/* entrypoints/content/style.css */
#tabnotes-ribbon {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: #f9d379;
color: #333;
padding: 8px 16px;
font-family: 'Sour Gummy', cursive;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: bold;
border-bottom-left-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
z-index: 999999;
}Key Properties:
position: fixed- Stays visible during scrollz-index: 999999- Appears above page contenttop: 0; right: 0- Top-right corner positioning
Importing CSS in Content Script
// entrypoints/content/index.ts
import './style.css';
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
main() {
const ribbon = document.createElement('div');
ribbon.id = 'tabnotes-ribbon';
ribbon.textContent = 'Note';
document.body.appendChild(ribbon);
}
});WXT automatically injects the CSS when the content script runs.
Conditional Ribbon Display
Problem: Ribbon currently shows on ALL pages, not just pages with notes.
Solution: Only inject ribbon if current page has a saved note.
Getting the Page Key
// entrypoints/content/index.ts
import './style.css';
const getPageKey = (url: string): string => {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
return urlObj.hostname + urlObj.pathname;
};
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
main() {
const pageKey = getPageKey(window.location.href);
console.log('Page key:', pageKey);
}
});window.location.href - Content scripts have access to page’s global window object.
Checking for Notes
Content scripts can access chrome.storage:
// entrypoints/content/index.ts
import './style.css';
import { storage } from 'wxt/storage';
const getPageKey = (url: string): string => {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
return urlObj.hostname + urlObj.pathname;
};
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
async main() {
const pageKey = getPageKey(window.location.href);
const notesStorage = await storage.getItem('sync:notesStorage');
// Only show ribbon if note exists
if (notesStorage?.[pageKey]?.note) {
const ribbon = document.createElement('div');
ribbon.id = 'tabnotes-ribbon';
ribbon.textContent = 'Note';
document.body.appendChild(ribbon);
}
}
});Testing:
- Visit page without note - no ribbon
- Open popup, save note
- Reload page - ribbon appears
Current Limitation: Requires page reload to see ribbon. We’ll fix this with messaging in Lesson 10.
Content Script Lifecycle
When Content Scripts Run
By default, content scripts run at document_idle - after DOM is complete but before all images load.
Other Options:
export default defineContentScript({
matches: ['https://*/*'],
runAt: 'document_start', // Before any DOM
// or
runAt: 'document_end', // After DOM, before images
// or
runAt: 'document_idle', // Default (recommended)
main() {
// ...
}
});For TabNotes: Use default document_idle - ensures document.body exists before injecting ribbon.
Avoiding Duplicate Ribbons
Problem: If script runs multiple times, multiple ribbons appear.
Solution: Check if ribbon already exists:
main() {
// Don't create duplicate ribbons
if (document.getElementById('tabnotes-ribbon')) return;
const pageKey = getPageKey(window.location.href);
// ... rest of logic
}Content Script Best Practices
Namespace Your Elements
Avoid ID/class collisions with page content:
/* ❌ Generic, might conflict */
#ribbon { ... }
/* ✅ Namespaced, less likely to conflict */
#tabnotes-ribbon { ... }Avoid Blocking Page Load
Keep content script logic lightweight:
// ❌ Slow, blocks page
await fetchLargeDataset();
await processExpensiveCalculation();
// ✅ Fast, doesn't block
const data = await storage.getItem('sync:notesStorage');
if (data[pageKey]) {
// Quick DOM manipulation
}What’s Next
Content scripts now inject visual indicators into web pages, but they only update on page load. Users must reload pages to see ribbon changes after saving notes.
Lesson 10 introduces the messaging API, allowing popup and background scripts to communicate with content scripts in real-time. This enables instant ribbon updates without page reloads.